Achieve this by acting as carriers of specific functional groups. Search the Dictionary for More Terms.

Solved The Enzyme Commission Developed A Classification Chegg Com
Coenzymes are often broadly called cofactors but they are chemically different.

. Which statement BEST describes a coenzyme. They are not capable of catalyze the reaction ut helps the enzyme to perform the recation by activating it. 1 n a small molecule not a protein but sometimes a vitamin essential for the activity of some enzymes Types.
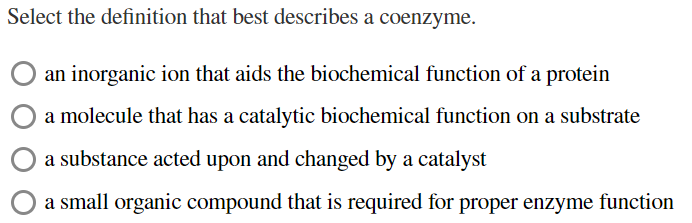
Which statement BEST describes the relationship between B12 and folate. A coenzyme is an organic non-protein compound that binds with an enzyme to catalyze a reaction. O an inorganic ion that aids the biochemical function of a protein O a molecule that has.
An enzyme is a protein that functions as a catalyst to mediate and speed a chemical reaction. A activate enzyme A B undergo phosphorylation C provide energy for the citric acid cycle D activate acyl groups for reaction E help break down macromolecules Answer. A substance often a vitamin that binds to an enzyme to facilitate enzyme activity.
Vitamin B12 activates folate and in turn activates itself. 28 Coenzyme A is a molecule whose function is to ________. Coenzyme is an organic compound which binds to apoenzyme the proteinaceous part of enzyme transiently.
A thermostable nonprotein compound that forms the active portion of an enzyme system after combination with an apoenzyme. Thus binding of apoenzyme enhances the enzymatic activity. It can be considered a helper molecule for a biochemical reaction.
Essential to metabolism of carbohydrates and. A coenzyme is a dissociable low-molecular weight non-proteinaceous organic compound often nucleotide participating in enzymatic reactions as acceptor or donor of chemical groups or electrons. The cofactor or coenzyme allows the reaction to happen quickly.
An organic molecule that assists with a proteins catalytic function O a molecule that has a catalytic biochemical function on a substrate O a molecule that is biochemically altered during a catalytic reaction O an inorganic ion that aids. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions and often require cofactors to function. A coenzyme cannot function alone but can be reused several times when paired with an enzyme.
An organic substance that reversibly combines with a specific protein the apoenzyme and with a substrate to form an active enzyme system. Many are produced from vitamins particularly water-soluble vitamins that have been phosphorylated. Coenzyme is a molecule necessary for catalysis of a chemical reaction by a specific enzyme.
Coenzymes are small nonproteinaceous molecules that provide a transfer site for a functioning enzyme. The function of coenzyme is to enhance the activity of enzyme. A substance that enhances the action of an enzyme.
This is a prime example of an enzyme working with a cofactor. Changes state over the course of a reaction unlike an enzyme not enzyme specific. D 29 Which coenzyme is reduced in.
Protein molecule that adds a specific chemical action to reaction catalyzed by enzymes that cannot be achieved by the 20 naturally occuring amino acids. H2COH HC0 EL - IV c 0 0 HO CH 0 HC0P-OH HC-0-P-OH -6 Which category does the catalyzing enzyme belong to. Coenzymes are small molecules.
A substance that enhances the action of an enzyme. When coenzymes attach to the active site of an enzyme called an apoenzyme and then create the active enzyme they engage in catalysis called holoenzyme. Coenzymes assist enzymes in turning substrates.
Among its constituents are pantothenic acid and a terminal SH group. Coenzyme Definition. An enzyme without a coenzyme is.
Apoenzyme along with the coenzyme forms holoenzyme which is the active form of enzyme. How many major classes of enzymes are there. Coenzyme A a coenzyme essential for carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
The binding usually occurs during catalysis of reaction and act in different directions. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to. Cocarboxylase thiamine pyrophosphate a coenzyme important in respiration in the Krebs cycle coenzyme A a coenzyme present in all living cells.
An enzyme is a protein that functions as a catalyst to mediate and speed a chemical reaction. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to. Coenzyme are small molecules that are inactive but when it binds with the protein molecule or called the apoenzyme it form the active enzyme ie Holoenzyme.
Seven four five eight Six Select the definition that best describes a coenzyme. Non-protein organic cofactors are called coenzymes. A coenzyme is a substance that works with an enzyme to initiate or aid the function of the enzyme.
Coenzymes are small molecules. Lyase ligase oxidoreductase transferase isomerase hydrolase Select the definition that best describes a coenzyme. Return to top of page.
Coenzyme ko-enzīm an organic molecule usually containing phosphorus and some vitamins sometimes separable from the enzyme protein. A coenzyme and an apoenzyme must unite in order to function as a holoenzyme. Coenzyme definition a molecule that provides the transfer site for biochemical reactions catalyzed by an enzyme.
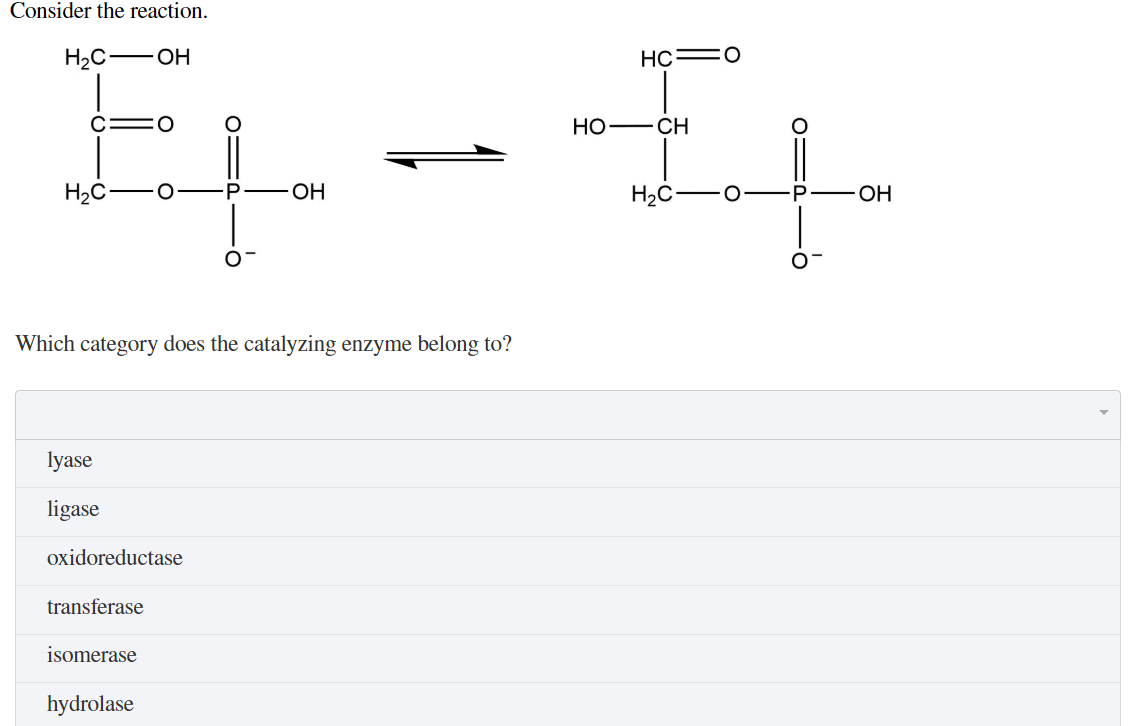
Solved Consider The Reaction H2c Oh Hc 0 El Iv C 0 0 Ho Chegg Com

Solved Please Please Make Sure The Answer Is Correct And Chegg Com
Solved Consider The Reaction H2c Oh Hc 0 El Iv C 0 0 Ho Chegg Com
0 Comments